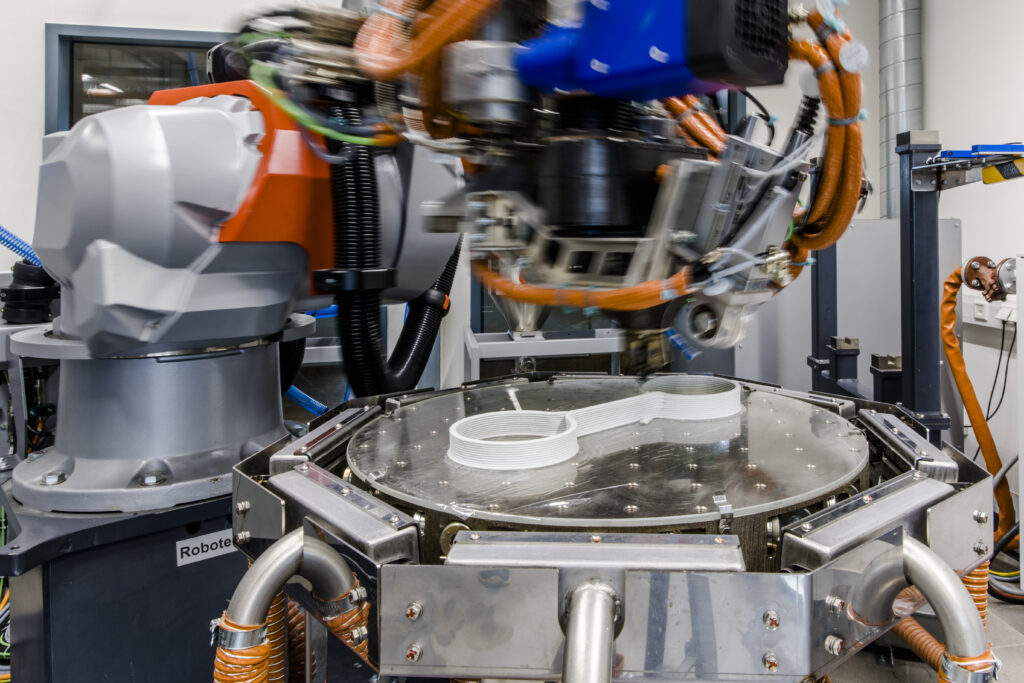
The production of large-volume components is of great importance in additive manufacturing, for which a dual robot system with two 6-axis robots is used. The focus here is particularly on functional integration. The parallel use of the two robots also allows the combination of additive and subtractive machining processes, which represents an efficient option for multi-stage production.
Additive manufacturing is ideally suited to providing the resulting component with extended functionalities during the manufacturing process. On the way to increasingly complex components, the flexible integration of inserts for maximum functional integration represents a major challenge. For example, there is a need for research into the insertion of metal inserts in the additive, polymer-based build-up process. Among other things, the suitable insertion strategies of the inserts play a relevant role here in order to enable pronounced functional integration.
The targeted local adaptation of component properties is also of great interest. The integration of continuous fibers offers great potential both for increasing mechanical properties in general and for the local, load-path-compliant reinforcement of highly stressed components. In combination with a 3D deposition, the latter also offers the possibility of compensating for mechanical properties that are less pronounced perpendicular to the material deposition, thus significantly expanding the range of applications.
To increase the efficiency of multi-stage manufacturing processes, the integration of post-processing steps and combined additive and subtractive processing is being worked on. The dual robot system is of great added value here, as different tools and processes can be used.
Due to the process, strand-based additive manufacturing methods generally result in a characteristic, wavy surface structure parallel to the strand deposition. Accordingly, functional surfaces require subsequent processing in compliance with defined position tolerances. To this end, investigations are being carried out into factors influencing the surface quality of the subtractively produced functional surfaces.
Samuel Schlicht, M.Sc., M.Sc.
Institute of Polymer Technology
Additive Manufacturing
- Phone number: +49 9131 85-71073
- Email: samuel.schlicht@fau.de